10 years of NITI Aayog
13 Jan, 2025
NITI Aayog celebrates 10 years of its Foundation
About NITI Aayog
· NITI Aayog, or the National Institution for Transforming India, was established on January 1, 2015.
· It is a premier policy think tank of the Government of India.
· It is created through a resolution of the union cabinet (i.e. neither constitutional nor statutory body).
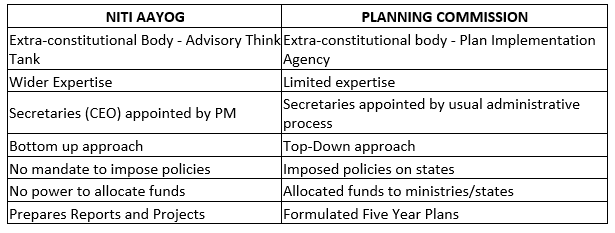
· It is a replacement for the Planning Commission of India
Main Objectives
Institutional Reforms
1. Cooperative Federalism: Foster cooperative federalism, promoting the involvement of state governments in the national development process.
2. Decentralized Planning: Encourage decentralized planning, allowing states to formulate their development plans.
Development Agenda
1. Inclusive Growth: Promote inclusive growth, focusing on poverty reduction, education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
2. Sustainable Development: Foster sustainable development, balancing economic growth with environmental protection and social equity.
3. Regional Development: Promote regional development, addressing disparities and imbalances across regions.
Strategic Direction
1. Directional and Strategic Input: Provide directional and strategic input to the development process, identifying key areas for reform and growth.
2. Incubator of Ideas: Act as an incubator of ideas, fostering innovation and experimentation in development policy and practice.
3. Monitoring and Evaluation: NITI Aayog monitors and evaluates the implementation of policies and programs.
4. Providing Technical Advice: It provides technical advice to the central and state governments on key policy issues.
Key Focus Areas
1. Poverty Elimination: Eliminate poverty, focusing on the most vulnerable sections of society.
2. Education and Skill Development: Promote education and skill development, enhancing employability and productivity.
3. Health and Nutrition: Improve health and nutrition outcomes, focusing on maternal and child health.
4. Infrastructure Development: Promote infrastructure development, including energy, transportation, and communication.
5. Environmental Protection: Foster environmental protection, promoting sustainable development and climate resilience.
Key Achievements
Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
· Initiatives like the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) and Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL) to foster innovation and entrepreneurship in India.
· Launched India Innovation Index
Cooperative Federalism:
· Initiatives, such as the Sub-Group of Chief Ministers on Skill Development and the Task Force on Agricultural Development.
· Assisted states in establishing State Institutions of Transformation (SITs) to improve governance and policy implementation.
· Launched Good Governance Index
Agricultural Development:
· Formulation of a Model Agricultural Land Leasing Act and the promotion of organic farming.
Digital Payments:
· It has encouraged the adoption of digital payments through initiatives like the Lucky Grahak Yojana and the Digi Dhan Vyapar Yojana.
Aspirational Districts Programme:
· It has launched the Aspirational Districts Programme to improve the socio-economic status of 112 districts across India.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
· It launched data drive indices like the SDG India Index and Composite Water Management Index
Energy and Resource:
· Launched e-AMIRT Portal (electrical vehicles) and Methanol Economy Programme
Composition of NITI Aayog
Governing Council
Chairperson: The Prime Minister of India
Members: Chief Ministers of all states and Lieutenant Governors of union territories
Special Invitees: Experts and specialists in various fields, invited by the Prime Minister
Vice-Chairperson
Appointment: Appointed by the Prime Minister
Role: Provides strategic direction and guidance to NITI Aayog
Members
Full-Time Members: Up to 2 full-time members, appointed by the Prime Minister
Part-Time Members: Up to 4 part-time members, appointed by the Prime Minister
Ex-Officio Members: Secretaries of various ministries and departments, as specified by the Prime Minister
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
Appointment: Appointed by the Prime Minister
Role: Head of the secretariat, responsible for implementing decisions and providing secretarial support
Secretariat
Composition: Comprises various departments and cells, including:
1. Research and Policy Division: Provides research and policy support
2. Economic Policy and Planning Division: Focuses on economic policy and planning
3. Infrastructure, Industry and Logistics Division: Works on infrastructure, industry, and logistics-related issues
4. Social Justice and Welfare Division: Focuses on social justice and welfare-related issues
5. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Division: Works on achieving the SDGs in India
6. International Cooperation Division: Handles international cooperation and diplomacy
Expert Groups and Task Forces
Constitution: Set up by the Prime Minister to provide expert advice on specific issues
Composition: Comprise experts and specialists from various fields
Specialized Wings
1. Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): Focuses on innovation and entrepreneurship
2. Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL): Promotes tinkering and innovation among school students
3. NITI Aayog's Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP): Supports women entrepreneurship and empowerment
Reason for replacement for Planning commission
1. Criticism of Centralized Planning: The Planning Commission was criticized for its centralized approach to planning, which often ignored the diverse needs and priorities of different states and regions.
2. Lack of Flexibility: It’s five-year plans were often rigid and inflexible, making it difficult to respond to changing economic and social circumstances.
3. Inadequate Representation: It’s was seen as being dominated by the central government, with inadequate representation from states and other stakeholders.
4. Overemphasis on Public Sector: It’s focus on public sector investment and planning was seen as outdated, given the increasing importance of the private sector in India's economy.
Key difference between NITI Aayog and Planning Commission